你好,我是陈皓,网名左耳朵耗子。
这节课,我们来学习一下函数式编程中非常重要的Map、Reduce、Filter这三种操作。这三种操作可以让我们轻松灵活地进行一些数据处理,毕竟,我们的程序大多数情况下都在倒腾数据。尤其是对于一些需要统计的业务场景来说,Map、Reduce、Filter是非常通用的玩法。
话不多说,我们先来看几个例子。
在下面的程序代码中,我写了两个Map函数,这两个函数需要两个参数:
[] string,说明需要处理的数据是一个字符串;func MapStrToStr(arr []string, fn func(s string) string) []string {
var newArray = []string{}
for _, it := range arr {
newArray = append(newArray, fn(it))
}
return newArray
}
func MapStrToInt(arr []string, fn func(s string) int) []int {
var newArray = []int{}
for _, it := range arr {
newArray = append(newArray, fn(it))
}
return newArray
}
整个Map函数的运行逻辑都很相似,函数体都是在遍历第一个参数的数组,然后,调用第二个参数的函数,把它的值组合成另一个数组返回。
因此,我们就可以这样使用这两个函数:
var list = []string{"Hao", "Chen", "MegaEase"}
x := MapStrToStr(list, func(s string) string {
return strings.ToUpper(s)
})
fmt.Printf("%v\n", x)
//["HAO", "CHEN", "MEGAEASE"]
y := MapStrToInt(list, func(s string) int {
return len(s)
})
fmt.Printf("%v\n", y)
//[3, 4, 8]
可以看到,我们给第一个 MapStrToStr() 传了功能为“转大写”的函数,于是出来的数组就成了全大写的,给MapStrToInt() 传的是计算长度,所以出来的数组是每个字符串的长度。
我们再来看一下Reduce和Filter的函数是什么样的。
func Reduce(arr []string, fn func(s string) int) int {
sum := 0
for _, it := range arr {
sum += fn(it)
}
return sum
}
var list = []string{"Hao", "Chen", "MegaEase"}
x := Reduce(list, func(s string) int {
return len(s)
})
fmt.Printf("%v\n", x)
// 15
func Filter(arr []int, fn func(n int) bool) []int {
var newArray = []int{}
for _, it := range arr {
if fn(it) {
newArray = append(newArray, it)
}
}
return newArray
}
var intset = []int{1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10}
out := Filter(intset, func(n int) bool {
return n%2 == 1
})
fmt.Printf("%v\n", out)
out = Filter(intset, func(n int) bool {
return n > 5
})
fmt.Printf("%v\n", out)
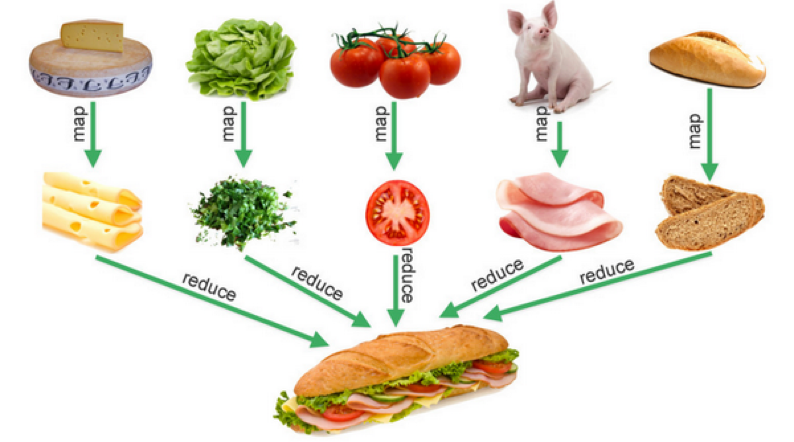
为了方便你理解呢,我给你展示一张图,它形象地说明了Map-Reduce的业务语义,在数据处理中非常有用。

通过刚刚的一些示例,你现在应该有点明白了,Map、Reduce、Filter只是一种控制逻辑,真正的业务逻辑是以传给它们的数据和函数来定义的。
是的,这是一个很经典的“业务逻辑”和“控制逻辑”分离解耦的编程模式。
接下来,我们来看一个有业务意义的代码,来进一步帮助你理解什么叫“控制逻辑”与“业务逻辑”分离。
首先,我们有一个员工对象和一些数据:
type Employee struct {
Name string
Age int
Vacation int
Salary int
}
var list = []Employee{
{"Hao", 44, 0, 8000},
{"Bob", 34, 10, 5000},
{"Alice", 23, 5, 9000},
{"Jack", 26, 0, 4000},
{"Tom", 48, 9, 7500},
{"Marry", 29, 0, 6000},
{"Mike", 32, 8, 4000},
}
然后,我们有下面的几个函数:
func EmployeeCountIf(list []Employee, fn func(e *Employee) bool) int {
count := 0
for i, _ := range list {
if fn(&list[i]) {
count += 1
}
}
return count
}
func EmployeeFilterIn(list []Employee, fn func(e *Employee) bool) []Employee {
var newList []Employee
for i, _ := range list {
if fn(&list[i]) {
newList = append(newList, list[i])
}
}
return newList
}
func EmployeeSumIf(list []Employee, fn func(e *Employee) int) int {
var sum = 0
for i, _ := range list {
sum += fn(&list[i])
}
return sum
}
简单说明一下:
EmployeeConutIf 和 EmployeeSumIf 分别用于统计满足某个条件的个数或总数。它们都是Filter + Reduce的语义。EmployeeFilterIn 就是按某种条件过滤,就是Fitler的语义。于是,我们就可以有接下来的代码了。
1.统计有多少员工大于40岁
old := EmployeeCountIf(list, func(e *Employee) bool {
return e.Age > 40
})
fmt.Printf("old people: %d\n", old)
//old people: 2
2.统计有多少员工的薪水大于6000
high_pay := EmployeeCountIf(list, func(e *Employee) bool {
return e.Salary > 6000
})
fmt.Printf("High Salary people: %d\n", high_pay)
//High Salary people: 4
3.列出有没有休假的员工
no_vacation := EmployeeFilterIn(list, func(e *Employee) bool {
return e.Vacation == 0
})
fmt.Printf("People no vacation: %v\n", no_vacation)
//People no vacation: [{Hao 44 0 8000} {Jack 26 0 4000} {Marry 29 0 6000}]
4.统计所有员工的薪资总和
total_pay := EmployeeSumIf(list, func(e *Employee) int {
return e.Salary
})
fmt.Printf("Total Salary: %d\n", total_pay)
//Total Salary: 43500
5.统计30岁以下员工的薪资总和
younger_pay := EmployeeSumIf(list, func(e *Employee) int {
if e.Age < 30 {
return e.Salary
}
return 0
})
刚刚的Map-Reduce都因为要处理数据的类型不同,而需要写出不同版本的Map-Reduce,虽然它们的代码看上去是很类似的。所以,这里就要提到泛型编程了。
我在写这节课的时候,Go语言还不支持泛型(注:Go开发团队技术负责人Russ Cox在2012年11月21golang-dev上的mail确认了Go泛型将在Go 1.18版本落地,时间是2022年2月)。所以,目前的Go语言的泛型只能用 interface{} + reflect来完成。interface{} 可以理解为C中的 void*、Java中的 Object ,reflect是Go的反射机制包,作用是在运行时检查类型。
下面,我们来看一下,一个非常简单的、不做任何类型检查的泛型的Map函数怎么写。
func Map(data interface{}, fn interface{}) []interface{} {
vfn := reflect.ValueOf(fn)
vdata := reflect.ValueOf(data)
result := make([]interface{}, vdata.Len())
for i := 0; i < vdata.Len(); i++ {
result[i] = vfn.Call([]reflect.Value{vdata.Index(i)})[0].Interface()
}
return result
}
我来简单解释下这段代码。
reflect.ValueOf() 获得 interface{} 的值,其中一个是数据 vdata,另一个是函数 vfn。vfn.Call() 方法调用函数,通过 []refelct.Value{vdata.Index(i)}获得数据。Go语言中的反射的语法有点令人费解,不过,简单看一下手册,还是能够读懂的。反射不是这节课的重点,我就不讲了。如果你还不太懂这些基础知识,课下可以学习下相关的教程。
于是,我们就可以有下面的代码——不同类型的数据可以使用相同逻辑的Map()代码。
square := func(x int) int {
return x * x
}
nums := []int{1, 2, 3, 4}
squared_arr := Map(nums,square)
fmt.Println(squared_arr)
//[1 4 9 16]
upcase := func(s string) string {
return strings.ToUpper(s)
}
strs := []string{"Hao", "Chen", "MegaEase"}
upstrs := Map(strs, upcase);
fmt.Println(upstrs)
//[HAO CHEN MEGAEASE]
但是,因为反射是运行时的事,所以,如果类型出问题的话,就会有运行时的错误。比如:
x := Map(5, 5)
fmt.Println(x)
代码可以很轻松地编译通过,但是在运行时却出问题了,而且还是panic错误……
panic: reflect: call of reflect.Value.Len on int Value
goroutine 1 [running]:
reflect.Value.Len(0x10b5240, 0x10eeb58, 0x82, 0x10716bc)
/usr/local/Cellar/go/1.15.3/libexec/src/reflect/value.go:1162 +0x185
main.Map(0x10b5240, 0x10eeb58, 0x10b5240, 0x10eeb60, 0x1, 0x14, 0x0)
/Users/chenhao/.../map.go:12 +0x16b
main.main()
/Users/chenhao/.../map.go:42 +0x465
exit status 2
所以,如果要写一个健壮的程序,对于这种用interface{} 的“过度泛型”,就需要我们自己来做类型检查。来看一个有类型检查的Map代码:
func Transform(slice, function interface{}) interface{} {
return transform(slice, function, false)
}
func TransformInPlace(slice, function interface{}) interface{} {
return transform(slice, function, true)
}
func transform(slice, function interface{}, inPlace bool) interface{} {
//check the `slice` type is Slice
sliceInType := reflect.ValueOf(slice)
if sliceInType.Kind() != reflect.Slice {
panic("transform: not slice")
}
//check the function signature
fn := reflect.ValueOf(function)
elemType := sliceInType.Type().Elem()
if !verifyFuncSignature(fn, elemType, nil) {
panic("trasform: function must be of type func(" + sliceInType.Type().Elem().String() + ") outputElemType")
}
sliceOutType := sliceInType
if !inPlace {
sliceOutType = reflect.MakeSlice(reflect.SliceOf(fn.Type().Out(0)), sliceInType.Len(), sliceInType.Len())
}
for i := 0; i < sliceInType.Len(); i++ {
sliceOutType.Index(i).Set(fn.Call([]reflect.Value{sliceInType.Index(i)})[0])
}
return sliceOutType.Interface()
}
func verifyFuncSignature(fn reflect.Value, types ...reflect.Type) bool {
//Check it is a funciton
if fn.Kind() != reflect.Func {
return false
}
// NumIn() - returns a function type's input parameter count.
// NumOut() - returns a function type's output parameter count.
if (fn.Type().NumIn() != len(types)-1) || (fn.Type().NumOut() != 1) {
return false
}
// In() - returns the type of a function type's i'th input parameter.
for i := 0; i < len(types)-1; i++ {
if fn.Type().In(i) != types[i] {
return false
}
}
// Out() - returns the type of a function type's i'th output parameter.
outType := types[len(types)-1]
if outType != nil && fn.Type().Out(0) != outType {
return false
}
return true
}
代码一下子就复杂起来了,可见,复杂的代码都是在处理异常的地方。我不打算Walk through 所有的代码,别看代码多,还是可以读懂的。
我来列一下代码中的几个要点。
Transform,这个来源于 C++ STL库中的命名。Transform(),一个是“就地完成” TransformInPlace()。Kind() 方法检查了数据类型是不是 Slice,函数类型是不是Func。verifyFuncSignature() 来完成的:NumIn()用来检查函数的“入参”;NumOut() :用来检查函数的“返回值”。reflect.MakeSlice() 来完成。好了,有了这段代码,我们的代码就很可以很开心地使用了:
1.可以用于字符串数组:
list := []string{"1", "2", "3", "4", "5", "6"}
result := Transform(list, func(a string) string{
return a +a +a
})
//{"111","222","333","444","555","666"}
2.可以用于整形数组:
list := []int{1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9}
TransformInPlace(list, func (a int) int {
return a*3
})
//{3, 6, 9, 12, 15, 18, 21, 24, 27}
3.可以用于结构体:
var list = []Employee{
{"Hao", 44, 0, 8000},
{"Bob", 34, 10, 5000},
{"Alice", 23, 5, 9000},
{"Jack", 26, 0, 4000},
{"Tom", 48, 9, 7500},
}
result := TransformInPlace(list, func(e Employee) Employee {
e.Salary += 1000
e.Age += 1
return e
})
同样,泛型版的 Reduce 代码如下:
func Reduce(slice, pairFunc, zero interface{}) interface{} {
sliceInType := reflect.ValueOf(slice)
if sliceInType.Kind() != reflect.Slice {
panic("reduce: wrong type, not slice")
}
len := sliceInType.Len()
if len == 0 {
return zero
} else if len == 1 {
return sliceInType.Index(0)
}
elemType := sliceInType.Type().Elem()
fn := reflect.ValueOf(pairFunc)
if !verifyFuncSignature(fn, elemType, elemType, elemType) {
t := elemType.String()
panic("reduce: function must be of type func(" + t + ", " + t + ") " + t)
}
var ins [2]reflect.Value
ins[0] = sliceInType.Index(0)
ins[1] = sliceInType.Index(1)
out := fn.Call(ins[:])[0]
for i := 2; i < len; i++ {
ins[0] = out
ins[1] = sliceInType.Index(i)
out = fn.Call(ins[:])[0]
}
return out.Interface()
}
同样,泛型版的 Filter 代码如下(同样分是否“就地计算”的两个版本):
func Filter(slice, function interface{}) interface{} {
result, _ := filter(slice, function, false)
return result
}
func FilterInPlace(slicePtr, function interface{}) {
in := reflect.ValueOf(slicePtr)
if in.Kind() != reflect.Ptr {
panic("FilterInPlace: wrong type, " +
"not a pointer to slice")
}
_, n := filter(in.Elem().Interface(), function, true)
in.Elem().SetLen(n)
}
var boolType = reflect.ValueOf(true).Type()
func filter(slice, function interface{}, inPlace bool) (interface{}, int) {
sliceInType := reflect.ValueOf(slice)
if sliceInType.Kind() != reflect.Slice {
panic("filter: wrong type, not a slice")
}
fn := reflect.ValueOf(function)
elemType := sliceInType.Type().Elem()
if !verifyFuncSignature(fn, elemType, boolType) {
panic("filter: function must be of type func(" + elemType.String() + ") bool")
}
var which []int
for i := 0; i < sliceInType.Len(); i++ {
if fn.Call([]reflect.Value{sliceInType.Index(i)})[0].Bool() {
which = append(which, i)
}
}
out := sliceInType
if !inPlace {
out = reflect.MakeSlice(sliceInType.Type(), len(which), len(which))
}
for i := range which {
out.Index(i).Set(sliceInType.Index(which[i]))
}
return out.Interface(), len(which)
}
最后,还有几个未尽事宜:
我个人觉得,Map、Reduce在数据处理的时候还是很有用的,Rob Pike可能平时也不怎么写“业务逻辑”的代码,所以,他可能也不太了解业务的变化有多么频繁……
当然,好还是不好,由你来判断,但多学一些编程模式,一定是对自己很有帮助的。
好了,这节课就到这里。如果你觉得今天的内容对你有所帮助,欢迎你帮我分享给更多人。