你好,我是景霄。
无论对于哪门语言,并发编程都是一项很常用很重要的技巧。比如我们上节课所讲的很常见的爬虫,就被广泛应用在工业界的各个领域。我们每天在各个网站、各个App上获取的新闻信息,很大一部分便是通过并发编程版的爬虫获得。
正确合理地使用并发编程,无疑会给我们的程序带来极大的性能提升。今天这节课,我就带你一起来学习理解、运用Python中的并发编程——Futures。
在我们学习并发编程时,常常同时听到并发(Concurrency)和并行(Parallelism)这两个术语,这两者经常一起使用,导致很多人以为它们是一个意思,其实不然。
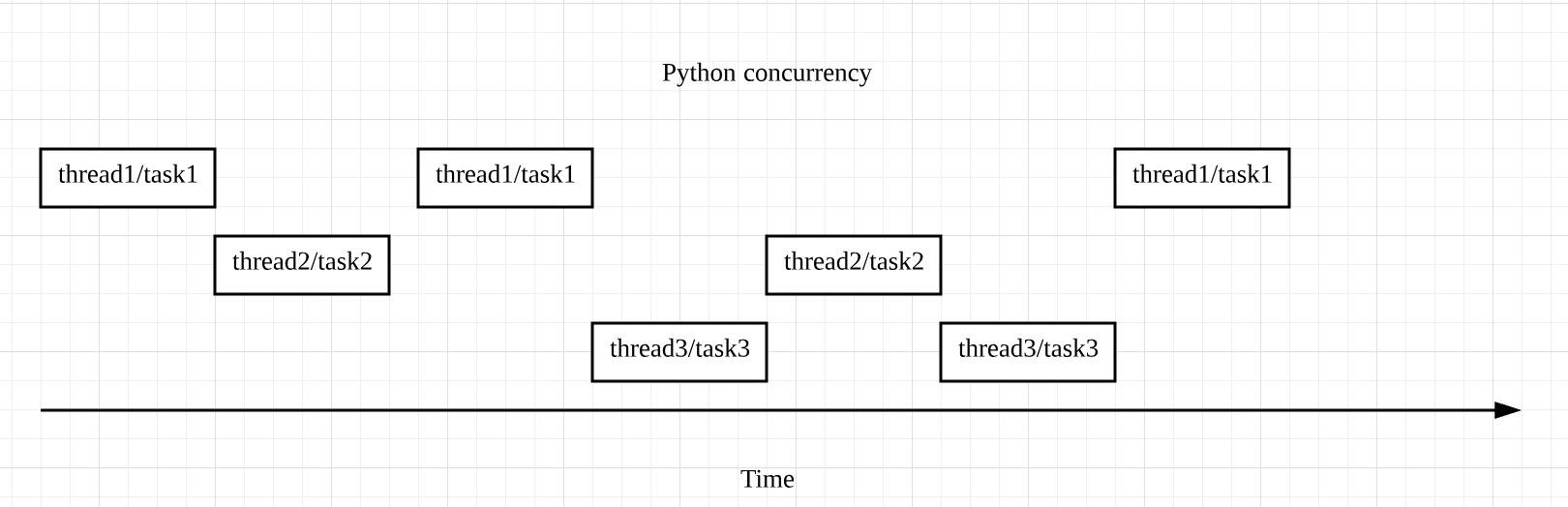
首先你要辨别一个误区,在Python中,并发并不是指同一时刻有多个操作(thread、task)同时进行。相反,某个特定的时刻,它只允许有一个操作发生,只不过线程/任务之间会互相切换,直到完成。我们来看下面这张图:

图中出现了thread和task两种切换顺序的不同方式,分别对应Python中并发的两种形式——threading和asyncio。
对于threading,操作系统知道每个线程的所有信息,因此它会做主在适当的时候做线程切换。很显然,这样的好处是代码容易书写,因为程序员不需要做任何切换操作的处理;但是切换线程的操作,也有可能出现在一个语句执行的过程中(比如 x += 1),这样就容易出现race condition的情况。
而对于asyncio,主程序想要切换任务时,必须得到此任务可以被切换的通知,这样一来也就可以避免刚刚提到的 race condition的情况。
至于所谓的并行,指的才是同一时刻、同时发生。Python中的multi-processing便是这个意思,对于multi-processing,你可以简单地这么理解:比如你的电脑是6核处理器,那么在运行程序时,就可以强制Python开6个进程,同时执行,以加快运行速度,它的原理示意图如下:
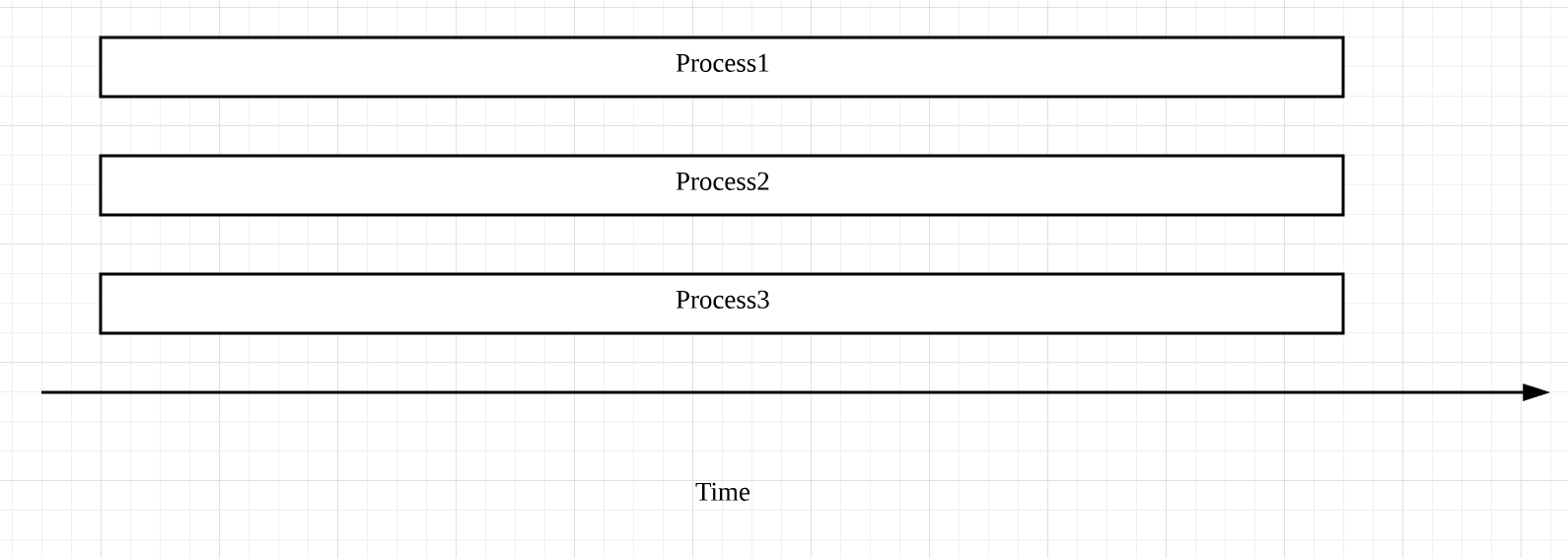
对比来看,
接下来,我们一起通过具体的实例,从代码的角度来理解并发编程中的Futures,并进一步来比较其与单线程的性能区别。
假设我们有一个任务,是下载一些网站的内容并打印。如果用单线程的方式,它的代码实现如下所示(为了简化代码,突出主题,此处我忽略了异常处理):
import requests
import time
def download_one(url):
resp = requests.get(url)
print('Read {} from {}'.format(len(resp.content), url))
def download_all(sites):
for site in sites:
download_one(site)
def main():
sites = [
'https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Portal:Arts',
'https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Portal:History',
'https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Portal:Society',
'https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Portal:Biography',
'https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Portal:Mathematics',
'https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Portal:Technology',
'https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Portal:Geography',
'https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Portal:Science',
'https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Computer_science',
'https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Python_(programming_language)',
'https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Java_(programming_language)',
'https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/PHP',
'https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Node.js',
'https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/The_C_Programming_Language',
'https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Go_(programming_language)'
]
start_time = time.perf_counter()
download_all(sites)
end_time = time.perf_counter()
print('Download {} sites in {} seconds'.format(len(sites), end_time - start_time))
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
# 输出
Read 129886 from https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Portal:Arts
Read 184343 from https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Portal:History
Read 224118 from https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Portal:Society
Read 107637 from https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Portal:Biography
Read 151021 from https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Portal:Mathematics
Read 157811 from https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Portal:Technology
Read 167923 from https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Portal:Geography
Read 93347 from https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Portal:Science
Read 321352 from https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Computer_science
Read 391905 from https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Python_(programming_language)
Read 321417 from https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Java_(programming_language)
Read 468461 from https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/PHP
Read 180298 from https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Node.js
Read 56765 from https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/The_C_Programming_Language
Read 324039 from https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Go_(programming_language)
Download 15 sites in 2.464231112999869 seconds
这种方式应该是最直接也最简单的:
我们可以看到总共耗时约2.4s。单线程的优点是简单明了,但是明显效率低下,因为上述程序的绝大多数时间,都浪费在了I/O等待上。程序每次对一个网站执行下载操作,都必须等到前一个网站下载完成后才能开始。如果放在实际生产环境中,我们需要下载的网站数量至少是以万为单位的,不难想象,这种方案根本行不通。
接着我们再来看,多线程版本的代码实现:
import concurrent.futures
import requests
import threading
import time
def download_one(url):
resp = requests.get(url)
print('Read {} from {}'.format(len(resp.content), url))
def download_all(sites):
with concurrent.futures.ThreadPoolExecutor(max_workers=5) as executor:
executor.map(download_one, sites)
def main():
sites = [
'https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Portal:Arts',
'https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Portal:History',
'https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Portal:Society',
'https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Portal:Biography',
'https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Portal:Mathematics',
'https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Portal:Technology',
'https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Portal:Geography',
'https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Portal:Science',
'https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Computer_science',
'https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Python_(programming_language)',
'https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Java_(programming_language)',
'https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/PHP',
'https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Node.js',
'https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/The_C_Programming_Language',
'https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Go_(programming_language)'
]
start_time = time.perf_counter()
download_all(sites)
end_time = time.perf_counter()
print('Download {} sites in {} seconds'.format(len(sites), end_time - start_time))
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
## 输出
Read 151021 from https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Portal:Mathematics
Read 129886 from https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Portal:Arts
Read 107637 from https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Portal:Biography
Read 224118 from https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Portal:Society
Read 184343 from https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Portal:History
Read 167923 from https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Portal:Geography
Read 157811 from https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Portal:Technology
Read 91533 from https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Portal:Science
Read 321352 from https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Computer_science
Read 391905 from https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Python_(programming_language)
Read 180298 from https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Node.js
Read 56765 from https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/The_C_Programming_Language
Read 468461 from https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/PHP
Read 321417 from https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Java_(programming_language)
Read 324039 from https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Go_(programming_language)
Download 15 sites in 0.19936635800002023 seconds
非常明显,总耗时是0.2s左右,效率一下子提升了10倍多。
我们具体来看这段代码,它是多线程版本和单线程版的主要区别所在:
with concurrent.futures.ThreadPoolExecutor(max_workers=5) as executor:
executor.map(download_one, sites)
这里我们创建了一个线程池,总共有5个线程可以分配使用。executer.map()与前面所讲的Python内置的map()函数类似,表示对sites中的每一个元素,并发地调用函数download_one()。
顺便提一下,在download_one()函数中,我们使用的requests.get()方法是线程安全的(thread-safe),因此在多线程的环境下,它也可以安全使用,并不会出现race condition的情况。
另外,虽然线程的数量可以自己定义,但是线程数并不是越多越好,因为线程的创建、维护和删除也会有一定的开销。所以如果你设置的很大,反而可能会导致速度变慢。我们往往需要根据实际的需求做一些测试,来寻找最优的线程数量。
当然,我们也可以用并行的方式去提高程序运行效率。你只需要在download_all()函数中,做出下面的变化即可:
with futures.ThreadPoolExecutor(workers) as executor
=>
with futures.ProcessPoolExecutor() as executor:
在需要修改的这部分代码中,函数ProcessPoolExecutor()表示创建进程池,使用多个进程并行的执行程序。不过,这里我们通常省略参数workers,因为系统会自动返回CPU的数量作为可以调用的进程数。
我刚刚提到过,并行的方式一般用在CPU heavy的场景中,因为对于I/O heavy的操作,多数时间都会用于等待,相比于多线程,使用多进程并不会提升效率。反而很多时候,因为CPU数量的限制,会导致其执行效率不如多线程版本。
Python中的Futures模块,位于concurrent.futures和asyncio中,它们都表示带有延迟的操作。Futures会将处于等待状态的操作包裹起来放到队列中,这些操作的状态随时可以查询,当然,它们的结果或是异常,也能够在操作完成后被获取。
通常来说,作为用户,我们不用考虑如何去创建Futures,这些Futures底层都会帮我们处理好。我们要做的,实际上是去schedule这些Futures的执行。
比如,Futures中的Executor类,当我们执行executor.submit(func)时,它便会安排里面的func()函数执行,并返回创建好的future实例,以便你之后查询调用。
这里再介绍一些常用的函数。Futures中的方法done(),表示相对应的操作是否完成——True表示完成,False表示没有完成。不过,要注意,done()是non-blocking的,会立即返回结果。相对应的add_done_callback(fn),则表示Futures完成后,相对应的参数函数fn,会被通知并执行调用。
Futures中还有一个重要的函数result(),它表示当future完成后,返回其对应的结果或异常。而as_completed(fs),则是针对给定的future迭代器fs,在其完成后,返回完成后的迭代器。
所以,上述例子也可以写成下面的形式:
import concurrent.futures
import requests
import time
def download_one(url):
resp = requests.get(url)
print('Read {} from {}'.format(len(resp.content), url))
def download_all(sites):
with concurrent.futures.ThreadPoolExecutor(max_workers=5) as executor:
to_do = []
for site in sites:
future = executor.submit(download_one, site)
to_do.append(future)
for future in concurrent.futures.as_completed(to_do):
future.result()
def main():
sites = [
'https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Portal:Arts',
'https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Portal:History',
'https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Portal:Society',
'https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Portal:Biography',
'https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Portal:Mathematics',
'https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Portal:Technology',
'https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Portal:Geography',
'https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Portal:Science',
'https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Computer_science',
'https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Python_(programming_language)',
'https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Java_(programming_language)',
'https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/PHP',
'https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Node.js',
'https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/The_C_Programming_Language',
'https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Go_(programming_language)'
]
start_time = time.perf_counter()
download_all(sites)
end_time = time.perf_counter()
print('Download {} sites in {} seconds'.format(len(sites), end_time - start_time))
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
# 输出
Read 129886 from https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Portal:Arts
Read 107634 from https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Portal:Biography
Read 224118 from https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Portal:Society
Read 158984 from https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Portal:Mathematics
Read 184343 from https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Portal:History
Read 157949 from https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Portal:Technology
Read 167923 from https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Portal:Geography
Read 94228 from https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Portal:Science
Read 391905 from https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Python_(programming_language)
Read 321352 from https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Computer_science
Read 180298 from https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Node.js
Read 321417 from https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Java_(programming_language)
Read 468421 from https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/PHP
Read 56765 from https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/The_C_Programming_Language
Read 324039 from https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Go_(programming_language)
Download 15 sites in 0.21698231499976828 seconds
这里,我们首先调用executor.submit(),将下载每一个网站的内容都放进future队列to_do,等待执行。然后是as_completed()函数,在future完成后,便输出结果。
不过,这里要注意,future列表中每个future完成的顺序,和它在列表中的顺序并不一定完全一致。到底哪个先完成、哪个后完成,取决于系统的调度和每个future的执行时间。
前面我说过,同一时刻,Python主程序只允许有一个线程执行,所以Python的并发,是通过多线程的切换完成的。你可能会疑惑这到底是为什么呢?
这里我简单提一下全局解释器锁的概念,具体内容后面会讲到。
事实上,Python的解释器并不是线程安全的,为了解决由此带来的race condition等问题,Python便引入了全局解释器锁,也就是同一时刻,只允许一个线程执行。当然,在执行I/O操作时,如果一个线程被block了,全局解释器锁便会被释放,从而让另一个线程能够继续执行。
这节课,我们首先学习了Python中并发和并行的概念与区别。
并发通常用于I/O操作频繁的场景,而并行则适用于CPU heavy的场景。
随后,我们通过下载网站内容的例子,比较了单线程和运用Futures的多线程版本的性能差异。显而易见,合理地运用多线程,能够极大地提高程序运行效率。
我们还一起学习了Futures的具体原理,介绍了一些常用函数比如done()、result()、as_completed()等的用法,并辅以实例加以理解。
要注意,Python中之所以同一时刻只允许一个线程运行,其实是由于全局解释器锁的存在。但是对I/O操作而言,当其被block的时候,全局解释器锁便会被释放,使其他线程继续执行。
最后给你留一道思考题。你能否通过查阅相关文档,为今天所讲的这个下载网站内容的例子,加上合理的异常处理,让程序更加稳定健壮呢?欢迎在留言区写下你的思考和答案,也欢迎你把今天的内容分享给你的同事朋友,我们一起交流、一起进步。
评论